Barcelona, Spain (UroToday.com) Sarcomatoid differentiation can occur in all subtypes of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and is associated with an aggressive phenotype. Sarcomatoid RCC (sRCC) is characterized by immunologic infiltration and has with higher PD-1/PD-L1 on tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating immune cells. JAVELIN Renal 101 demonstrated a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) with avelumab plus axitinib (A + Ax) versus sunitinib (median PFS 13.8 vs 8.4 months, HR 0.69, p < 0.001) in patients with previously untreated clear cell mRCC.1 This abstract reports the efficacy and biomarker results from a post-hoc analysis of patients enrolled in JAVELIN Renal 101 who had sarcomatoid features in their tumor histology.
The study design is shown below. Eligible patients had treatment-naïve unresectable metastatic RCC (mRCC) with measurable disease. All Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) and International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) risk groups were eligible. Patients were randomized 1:1 to A + Ax versus sunitinib and stratified by ECOG performance status and geographic region. Co-primary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the PD-L1 positive cohort. PFS and OS in the overall cohort was a key secondary endpoint.
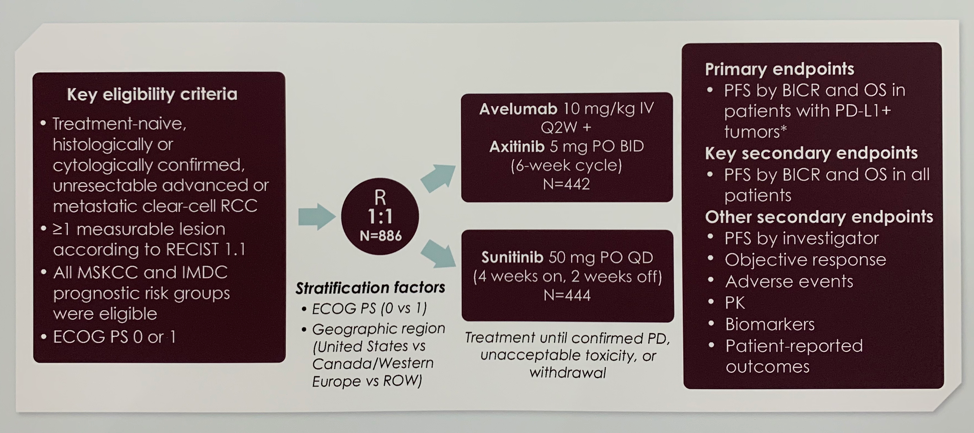
Of 886 patients with mRCC enrolled in JAVELIN Renal 101, 108 (12.2%) had sarcomatoid components and/or features in their pathology report, 47 in the A + Ax arm and 61 in the sunitinib arm. Baseline characteristics in this subgroup were well-balanced between treatment arms and consistent with the overall trial population. The only notable difference between the two treatment groups in the sRCC population is that the PD-L1 positive status was significantly lower in patients who received A + Ax (72.3%) versus sunitinib (85.2%).
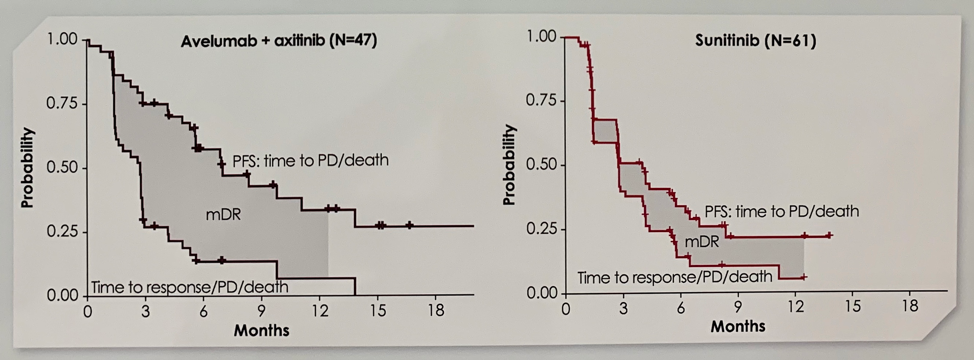
Patients with sRCC had an improved PFS of 7.0 months in the A + Ax arm compared to 4.0 months in the sunitinib arm (stratified HR 0.57, 0.325-1.003).

The 12-month OS rate was 83.0% with the combination and 67.0% with sunitinib. The confirmed objective response rate was higher in the A + Ax arm (46.8%) than the sunitinib arm (21.3%). Further, patients in the combination arm had 2.4 months longer median duration of response than those in the sunitinib arm.
The investigators reported results of multiple biomarker analyses, which revealed that sRCC tumors had an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and higher CD274 and CD8A gene expression. Further, they discovered that approximately 50% of sRCC patients in this cohort had m3 tumors based on the subtype-specific mRNA signatures from molecular analysis of clear cell RCC tumors by the TCGA;2 m3 is the molecular subset of RCC tumors associated with the poorest survival. Similar to results from the overall population, patients with sRCC who had m3 tumors that were also CD8- or CD8A-positive had longer median PFS with A + Ax (6.2 and 8.3 months) than sunitinib (2.9 and 2.8 months). These characteristics may help explain the poorer prognosis of sRCC patients when treated with VEGF inhibitor alone, but comparable response to the overall cohort when treated with A + Ax.
In conclusion, this study found that patients with sRCC who received A + Ax had PFS and ORR benefit over sunitinib, consistent with the results in the overall trial population. This analysis provides insight into the biology of an aggressive subtype of RCC and suggests a potential new treatment option.
Presented by: Toni K. Choueiri, MD, Director of the Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology, Director of the Kidney Cancer Center, the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Jerome and Nancy Kohlberg Chair, Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts
Written by: Jacob Berchuck, MD, Medical Oncology Fellow at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Twitter: @jberchuck at the 2019 European Society for Medical Oncology annual meeting, ESMO 2019 #ESMO19, 27 Sept – 1 Oct, 2019 in Barcelona, Spain
References:
- Motzer, Robert J., Konstantin Penkov, John Haanen, Brian Rini, Laurence Albiges, Matthew T. Campbell, Balaji Venugopal et al. “Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma.” New England Journal of Medicine 380, no. 12 (2019): 1103-1115.
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. “Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.” Nature 499, no. 7456 (2013): 43.
